Mosswholesale
Terrarium Umbrella liverwort with Phytosanitary certification and Passport, grown by moss supplier
Terrarium Umbrella liverwort with Phytosanitary certification and Passport, grown by moss supplier
Impossible de charger la disponibilité du service de retrait
Delivery information: We ship with DHL for orders of 100euros and more we give free shipping, for small orders we ship with Laposte. We will be sending plant passports with each species, your order will arrive in 2-3 days with DHL.
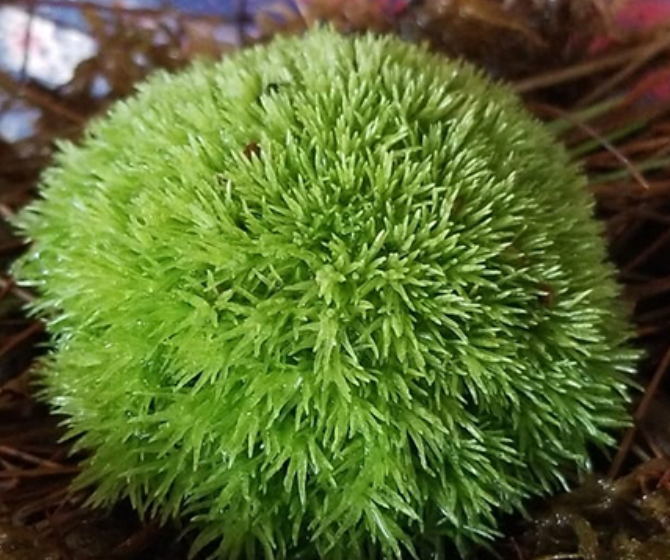
Marchantia polymorphaas Is a partial shade high humidity moss that loves lots of nitrogen fertiliser, she grows on acidic soils
We sell Marchantia polymorphaas spores and mother plant in a mixture of agra-agra cloning agent and sterilized water.
These syringes are easy to use, just mix with potting soil and spread over rock or spread into a carpet, will grow after 3 weeks into tiny liverwort that then connect together into a carpet and spread from there. The benefit of growing from spores is they grow and thrive in the environment, if terrarium or moss garden, or water feature.
we also sell the correct "Growing Substrate" for Marchantia polymorphan different quantities to help you give your Liverwort the best environment.
Please watch this video on how we collect liverwort spores https://youtu.be/env6tpYWs5U
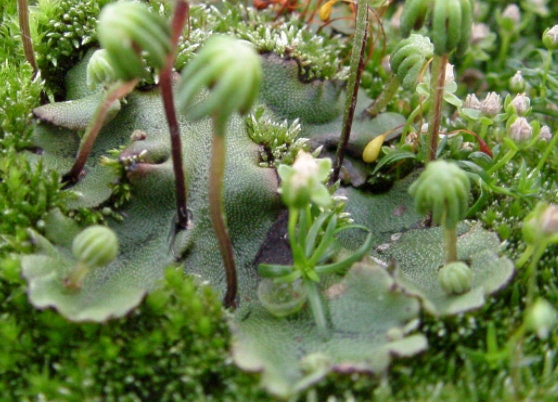
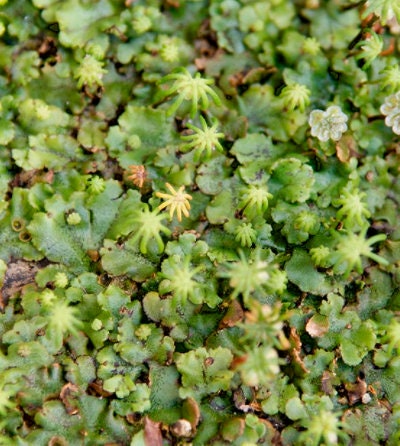
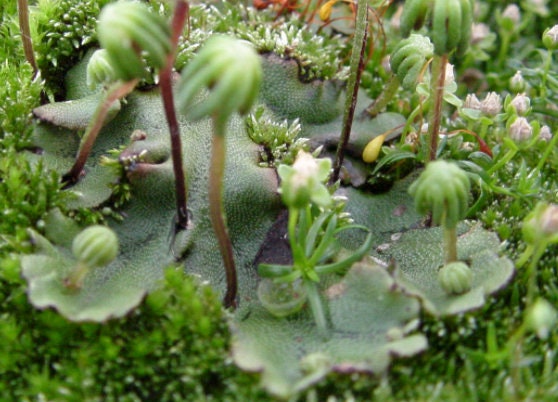
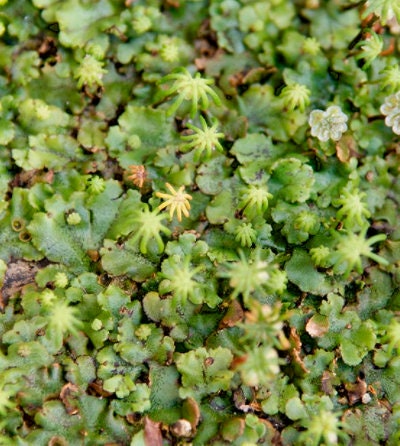
It is a thallose liverwort that forms a rosette of flattened thalli with forked branches. The thalli grow up to 10 cm long with a width of up to 2 cm. It is usually green in color but older plants can become brown or purplish. The upper surface has a pattern of polygonal markings. The underside is covered by many root-like rhizoids which attach the plant to the soil. The plants produce umbrella-like reproductive structures known as gametophores. The gametophores of female plants consist of a stalk with star-like rays at the top. These contain archegonia, the organs which produce the ova. Male gametophores are topped by a flattened disc containing the antheridia which produces sperm. This species reproduces asexually by gemmae that are produced within gemmae cups. Gemmae are lentil shaped and are released by droplets of water. Plants produced in this way can expand a patch significantly.
Your order will be packed safely and I'll send your Internation tracking number so you can follow your order travels to you :)
This carpeting plant is great for moist habitat terrariums. Liverwort loves to be as close to the water, water running over it, and can be submerged at a shallow depth. Your fish, lizards, frogs, and snakes will love this plant. You will receive 10cm x 10cm of Liverwort. There have been occasions where the Liverwort has been stopped at the board of the USA this happens rarely, please be aware that you purchase at and low risk of this.
Please watch this video for more info about how we grow liverwort and how to propagate: https://youtu.be/env6tpYWs5U
How To Grow
Liverwort can be grown in a moist terrarium, aquarium, or in small plastic boxes on the windowsill, as long as it is not too hot. These locations allow for better-controlled growth conditions and modifications to allow as much expansion as possible. A good source of light and some added CO2 can kick liverworts’ growth rate to an accelerated new level.
The most effective method to cultivate Liverwort is pretty much the same as Crystalwort. The parent plant should be divided into smaller pieces and then be tied down to a mesh or surface with thread or fishing string. Doing so will ensure that the flora remains attached. Liverwort is known for breaking off and dispersing throughout the tank. Those pieces should also be able to regenerate on their own. Although, such an occurrence can create some unwanted disarray in an aquarium.
Watering
Liverwort is a type of plant that will require a large quantity of water. When grown submerged it will not need to be watered. The plant will be able to absorb as much water and nutrients as it needs on its own. Unlike Crystalwort or most mosses, Liverwort will not benefit from a steady water flow. Since the plant can break off easily, too much water movement can make the situation worst.
Adding diversity to an enclosure is key to an aesthetically pleasing enclosure. Try mixing up the look of your vivarium with different flora that can easily co-exist in the same types of environment.
Historically, three taxonomic bryophyte groups have been recognized and now represent the three main divisions in this group: Marchantiophyta (liverworts), Bryophyta (mosses) and Anthocerotophyta (hornworts). The three main groups have diversified throughout their evolutionary history, making it difficult to identify the specific characters separating these three groups.
The status of bryophytes as the oldest living land plants is widely accepted.
Marchantia, genus of liverworts (creeping ribbonlike plants) in the order Marchantiales, commonly found on moist clay or silty soils, especially on recently burned land throughout the Northern Hemisphere. Dark green Marchantia gametophytes are branched and ribbonlike, about 1.3 cm (0.5 inch) wide and 5 to 13 cm long. The diamond-shaped markings on their upper surfaces, signs of interior air chambers, have a central pore through which air diffuses.
Male and female plants have umbrella-like, stalked reproductive structures. The male structures are disk-shaped with scalloped edges; the female structures have nine fingerlike projections. Sperm produced by male plants are splashed by raindrops onto female plants. Sporophytes (asexual plants) develop from fertilized eggs in the female structures. Vegetative reproduction occurs in both male and female plants by means of rounded, fringed gemmae (asexual buds) or by pieces of the plant body that may break off and grow.
Starting with Greek philosophers such as Aristotle and Theophrastus, this species had been mentioned in the herbal literature long before modern plant taxonomic study was applied. The name ‘liverwort’ is derived from the liver-shaped form of thalloid liverworts such as Marchantia. In the Middle Ages in Europe, Marchantia was thought to be useful for treating diseases of the liver on the basis of the ‘doctrine of signatures’, by which a plant resembling a human organ was thought to be useful in treating diseases of that organ ( Schuster 1966 ). In the 19th century, M. polymorpha was already one of the most studied species in plant science. The developing thallus, sporeling and gemmaling have been continuously used for nearly 200 years to study morphological and physiological responses to various environmental factors
Materials
Materials
Shipping & Returns
Shipping & Returns
Dimensions
Dimensions
Care Instructions
Care Instructions


-
Free Shipping
We offer free shipping in France! and internationally for orders of 500 euros or more.


